Cryptocurrencies
Table of Contents
1 Crypto Basic
1.1 Hash Function
- takes any string as input
- fixed-size output
- efficiently computable (
O(n)for n-bit string)
for crypto security, additional three features:
- collision-resistance
- hiding
- puzzle-friendliness
1.2 Hash Pointers
Pointer to where some info is stored, and hash of the info
1.2.1 Data Structure with Hash Pointers
- Block Chain: Hash pointer with linked list
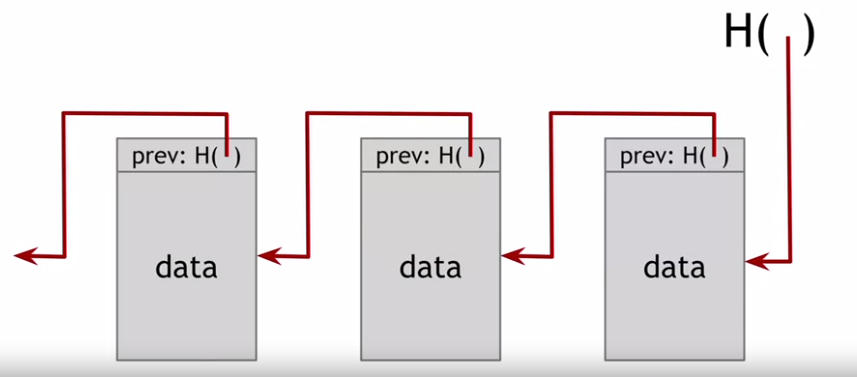
- Merkle Tree: Hash pointer with binary tree
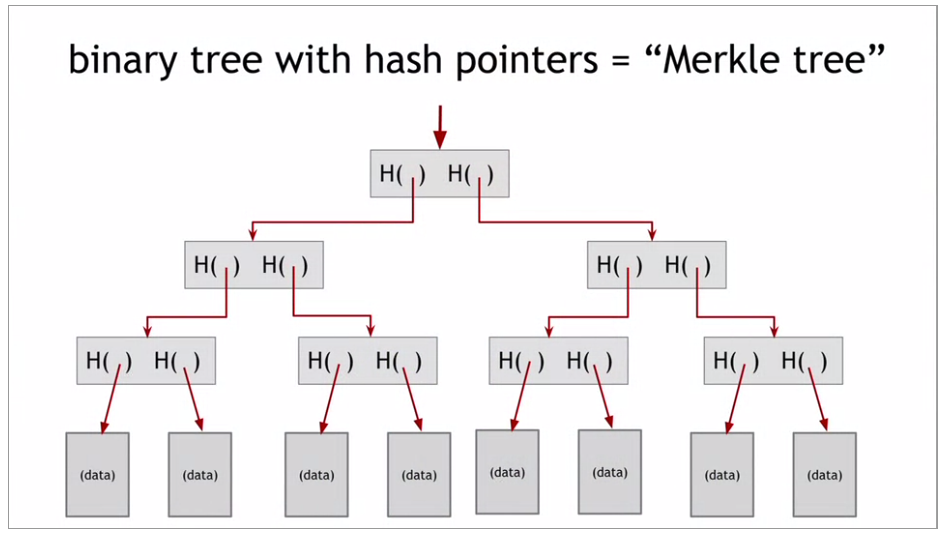
1.3 Digital Signatures
1.3.1 APIs
(sk, pk) := generateKeys(keysize)sig := sign(sk, message)isValid := verify(pk, message, sig)